WordPress Login Hardening Checklist (2026 Guide)
The WordPress login page is the most targeted entry point on any site, making its protection a core security requirement, not an optional task.
Attackers routinely use brute-force attempts, credential stuffing, and automated bots to exploit weak or exposed login endpoints.
In this post, I will provide a practical framework for WordPress login hardening, covering securing the login URL, enforcing HTTPS, using strong passwords, enabling two-factor authentication, implementing access controls, and enabling activity monitoring.
By applying these configurations and operational safeguards, site owners can reduce the risk of unauthorized access.
Ultimately, it can help you maintain a resilient authentication layer across any WordPress environment.
Table of Contents
The WordPress Hardening Checklist You Can Follow
Here is the complete WordPress login hardening checklist for you to follow and implement accordingly:
1. Secure the Login Endpoint
The WordPress login endpoint is a constant target for bots and brute-force attempts, so its protection must start at the perimeter.
Always enforce HTTPS to secure credentials in transit, and redirect all HTTP requests to HTTPS.
Changing the default `/wp-login.php` path or using a custom login slug helps reduce noise from automated scanners targeting the default URL.
Apply rate limiting or firewall rules to block repeated login attempts, restrict access by IP or region, and deny traffic from known malicious sources.
When possible, limit direct access to `/wp-admin` for unauthenticated users and require authentication via controlled gateways.
These measures collectively reduce exposure, filter unwanted traffic early, and lower the chance of successful login exploitation.
Login hardening only works if it’s implemented consistently across your stack. Rate limiting, CAPTCHA, lockouts, and MFA/SSO need to match your user roles and access patterns.
When you treat this as part of broader WordPress security, it’s easier to standardize controls (login URL policy, redirects, audit logs) and avoid conflicts caused by overlapping plugins.
2. Enforce Strong Authentication Controls
Strong authentication controls form the foundation of WordPress login hardening, preventing most account-based compromises before they begin.
Enforce strict password requirements, including length, complexity, and uniqueness, to prevent credentials from being easily guessed or reused across multiple platforms.
Discourage shared or generic admin accounts, as they eliminate traceability and increase exposure.
Implement mandatory two-factor authentication (2FA) for all users with elevated privileges, administrators, editors, and site managers, to ensure that even if a password is stolen, access cannot be gained without a secondary verification step.
Use plugins or hosting-level tools to set login attempt limits and enforce cooldown periods after multiple failures, deterring brute-force and credential-stuffing attacks.
Regularly audit user passwords and authentication logs to identify weak credentials or repeated failures.
Protect password recovery flows by verifying ownership via email or secondary approval steps, and disable unnecessary login vectors like XML-RPC if they’re not in use.
Combined, these authentication policies close the most common entry points exploited in WordPress compromises and ensure that only verified users can reach the dashboard.
3. Restrict User Access and Privileges
Restricting user access and privileges minimizes the number of potential attack targets and limits the damage if a single account is compromised.
Begin by auditing all user accounts and removing inactive or unnecessary ones, especially those with administrative privileges.
Apply the principle of least privilege: each user should have only the access required for their role.
Convert outdated administrator accounts to lower roles when full access is no longer needed, and ensure that only a small, trusted group retains administrative rights.
Review WordPress roles and capabilities regularly, and use role management plugins if finer control is required.
Disable or restrict XML-RPC if it’s not actively used for integrations, as it can be exploited for brute-force or distributed login attacks.
In multisite or multi-user environments, enforce strict account separation between staging and production systems.
By tightening access boundaries, you reduce the number of high-value credentials exposed to attackers and limit the impact of any breach to the smallest possible surface area.
4. Monitor, Log, and Respond to Login Activity
Monitoring and logging login activity turns security from a static setup into an active defense system.
Every WordPress site should record both successful and failed login attempts, along with timestamps, IP addresses, and user identifiers.
These logs reveal attack patterns, such as repeated login failures, 2FA denials, or unusual access times.
Configure real-time alerts for suspicious behavior, such as logins from new countries or sudden spikes in failed login attempts, so administrators can respond before damage occurs.
Integrate WordPress login logs with your hosting platform, SIEM, or security plugin to centralize visibility and streamline incident response.
Review lockout records to ensure they reflect real attacks rather than false positives, and investigate repeated access from the same source.
For larger installations, automate response actions such as IP blocking or forced password resets for compromised users.
Continuous monitoring ensures that login protections remain effective and that any abnormal behavior is caught before it escalates into a breach.
5. Keep the Login Stack Updated and Tested
Keeping the login stack up to date and validated ensures that protections remain effective over time.
WordPress core, themes, and plugins should always run on the latest stable versions, as many updates include critical security fixes affecting authentication and session handling.
Remove any abandoned plugins, especially those that integrate with login or user management, as outdated code can create backdoors for attackers.
After each update or hosting change, test the login process to confirm that HTTPS, 2FA, rate limiting, and custom login rules still function as intended.
Schedule periodic security reviews to verify that configuration changes, caching layers, or new plugins haven’t weakened protections.
Reassess password policies and access rules as your team or site grows. Login security can silently erode through neglect.
Regular updates, testing, and verification, however, preserve the integrity of your authentication system and ensure consistent defense against evolving attack methods.
How LoginPress Helps with WordPress Login Hardening
Keeping your login stack up to date and validated ensures your site’s protections remain effective over time.
WordPress core, themes, and plugins should always run on the latest stable versions, as many updates include critical security fixes targeting authentication and session handling vulnerabilities.
LoginPress plays a vital role in this maintenance cycle by centralizing and hardening your entry points.
Instead of relying on fragmented, unmaintained code snippets that can break during core updates, LoginPress provides a professional-grade framework designed specifically for WordPress login hardening.
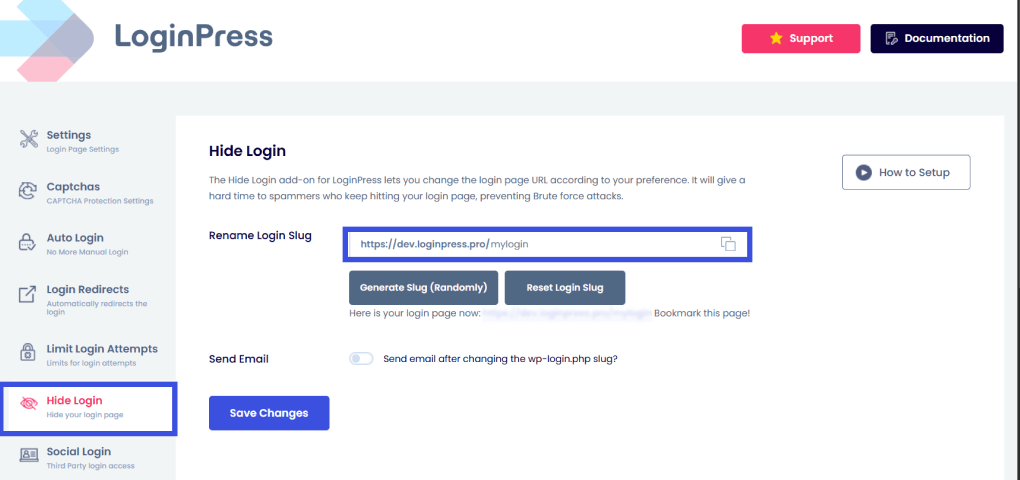
1. By using the LoginPress Hide Login add-on, you can obscure the standard /wp-admin URL. This effectively neutralizes automated bot attacks targeting default paths, removing your site from attackers’ “low-hanging fruit” list.
2. Intelligent Rate Limiting: LoginPress allows you to limit login attempts WordPress and enforce a strict lockout policy. By configuring custom Lockout Minutes, for example, banning an IP for 24 hours after 3 failed attempts within 5 minutes, you effectively kill brute-force scripts before they can guess a password.
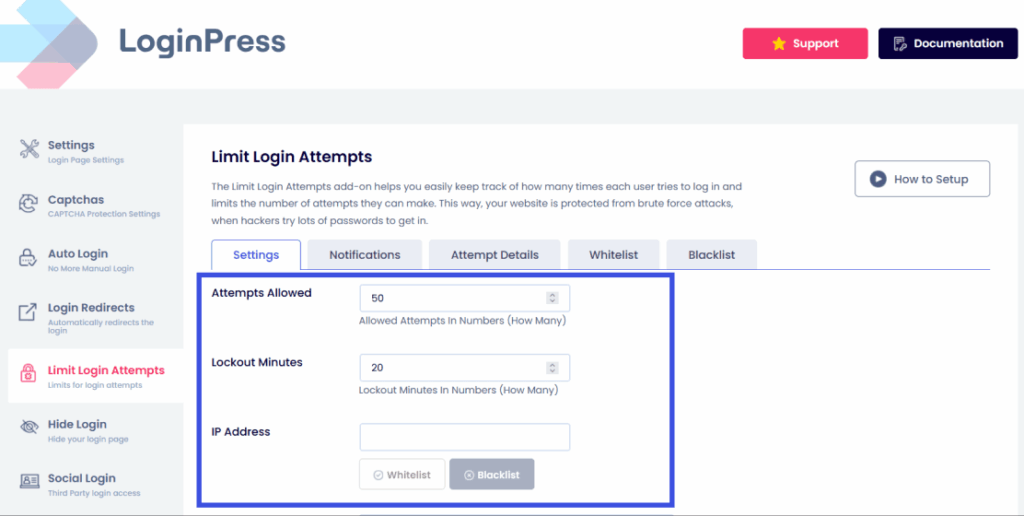
This effectively kills brute-force scripts before they can guess a password, hence hardening WordPress.
This simple shift is a powerful defense for login security for WordPress against username harvesting and credential stuffing attacks.
3. Masking Vulnerabilities: You can replace specific, descriptive error messages with generic alerts. This simple shift is a powerful defense against username harvesting and credential stuffing attacks, as it prevents attackers from confirming whether a specific username exists.

Login security can erode silently through neglect; however, combining regular updates with the active verification and hardening features of LoginPress helps preserve the integrity of your authentication system against evolving attack methods.
FAQs on Secure WordPress Login
What is WordPress Login Hardening, and why is it necessary in 2026?
WordPress Login Hardening is the process of securing your website’s authentication entry points to prevent unauthorized access. In 2026, standard passwords are no longer enough because attackers use AI-powered scripts to perform high-speed “credential stuffing” and brute-force attacks. Hardening involves adding multiple layers of defense, such as LoginPress for custom URLs and error masking, to ensure that even if a password is leaked, your site remains impenetrable.
How does changing the default WordPress login URL improve security?
By default, every WordPress site uses /wp-login.php or /wp-admin. Bots scan millions of sites per hour, looking for these specific paths to launch attacks. Changing your login URL (often called “URL masking” or “hiding”) is a powerful deterrent, as it removes your site from the automated “hit list” of most botnets. Using a tool like LoginPress lets you easily rename this path without breaking your site’s core functionality.
What are the most critical items on a WordPress login hardening checklist?
A modern WordPress Hardening Checklist should prioritize “layered” security. The most critical items include:
Enforcing Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): The single most effective way to stop account takeovers.
Limiting Login Attempts: To thwart brute-force scripts.
Renaming the Login Slug: To hide the entry door from bots.
Idle Session Logout: Automatically logs out users after a period of inactivity to prevent session hijacking.
Regular Audits: Removing abandoned plugins and updating the “Login Stack” (Core, LoginPress, and 2FA tools) weekly.
Conclusion: WordPress Login Hardening
Implementing a WordPress login hardening strategy is no longer optional in 2026. It is the foundation of a resilient website.
By following a comprehensive WordPress hardening checklist, you can transform your site from a vulnerable target into a digital fortress.
As we’ve explored, login security for WordPress is most effective when layered. The goal is the same: create a secure WordPress login environment that keeps unauthorized users out and ensures a seamless experience for your team.
Hardening WordPress is an ongoing process. By prioritizing authentication security, hiding your login paths, and committing to regular updates, you keep your site ahead of evolving threats.
Do not let your security erode through neglect; take these steps today to preserve your site’s integrity for the long term. That is all for this post.
For more related posts, check:
- How to Manage Multiple Login Methods in WordPress (Without Confusing Users)
- Top WordPress Management Software Every Website Owner Should Know (2026)
- WordPress Login Optimization for Better User Retention (Explained)
When was the last time you checked your site’s access logs? Are you seeing legitimate logins, or is a botnet currently knocking on your door?



